Django是一个免费的开源高级Web框架,用于开发Python Web应用程序。它带有一组工具,可帮助您构建安全且可扩展的Web应用程序。它的主要目标是简化复杂应用程序的创建并维护内部结构。
在本教程中,我们将学习如何在CentOS 8上安装Django并将Nginx配置为Django的反向代理。
先决条件
- 运行CentOS的服务器8。
- 在您的服务器上配置了root密码。
安装必需的软件包
Django是一个基于Python的框架,因此您需要在系统中安装Python和PIP。您可以通过运行以下命令来安装它们:
dnf install python36 python3-pip -y一旦安装了两个软件包,就可以继续进行下一步。
安装Django
您可以使用PIP命令安装Django,如下所示:
pip3 install Django安装Django之后,您可以使用以下命令检查Django的版本:
django-admin --version您应该在以下输出中看到Django版本:
3.0.3
创建一个Django项目
至此,Django已安装。现在,该创建一个新的Django应用程序了。
您可以使用/ opt目录中的django-admin命令创建一个新的Django应用程序,如下所示:
cd /opt
django-admin startproject djangoproject创建django项目后,将目录更改为djangoproject并使用以下命令迁移更改:
cd djangoproject
python3 manage.py migrate您应该获得以下输出:
Operations to perform: Apply all migrations: admin, auth, contenttypes, sessions Running migrations: Applying contenttypes.0001_initial... OK Applying auth.0001_initial... OK Applying admin.0001_initial... OK Applying admin.0002_logentry_remove_auto_add... OK Applying admin.0003_logentry_add_action_flag_choices... OK Applying contenttypes.0002_remove_content_type_name... OK Applying auth.0002_alter_permission_name_max_length... OK Applying auth.0003_alter_user_email_max_length... OK Applying auth.0004_alter_user_username_opts... OK Applying auth.0005_alter_user_last_login_null... OK Applying auth.0006_require_contenttypes_0002... OK Applying auth.0007_alter_validators_add_error_messages... OK Applying auth.0008_alter_user_username_max_length... OK Applying auth.0009_alter_user_last_name_max_length... OK Applying auth.0010_alter_group_name_max_length... OK Applying auth.0011_update_proxy_permissions... OK Applying sessions.0001_initial... OK
接下来,您将需要创建一个用于管理Django项目的管理员用户帐户。您可以使用以下命令创建它:
python3 manage.py createsuperuser系统将要求您提供用户名,电子邮件和密码。您可以根据自己的选择提供它们,如下所示:
Username (leave blank to use 'root'): dadmin Email address: admin@example.com Password: Password (again): Superuser created successfully.
完成后,您可以继续下一步。
启动Django应用程序
默认情况下,无法从远程主机访问Django应用程序。因此,您将需要允许Django用于外部主机。您可以通过在settings.py中添加服务器IP来实现:
nano /opt/djangoproject/djangoproject/settings.py更改以下行:
ALLOWED_HOSTS = ['your-server-ip']
保存并关闭文件。然后,使用以下命令启动Django应用程序:
cd /opt/djangoproject
python3 manage.py runserver 0.0.0.0:8000您应该看到以下输出:
Watching for file changes with StatReloader Performing system checks... System check identified no issues (0 silenced). March 03, 2020 - 02:31:19 Django version 3.0.3, using settings 'djangoproject.settings' Starting development server at http://0.0.0.0:8000/ Quit the server with CONTROL-C. Django application is now started and runs on port 8000.
至此,Django应用程序现在已启动并在端口8000上运行。您现在可以继续执行下一步。
配置SELinux和防火墙
接下来,您将需要允许端口8000和80通过Firewalld。您可以使用以下命令允许它们:
firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=8000/tcp
firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=80/tcp
firewall-cmd --reload
接下来,使用以下命令配置SELinux:
setsebool httpd_can_network_connect on -P完成后,您可以继续下一步。
访问Django应用程序
您可以通过访问URL http:// your-server-ip:8000来访问Django应用程序。您应该看到以下页面:
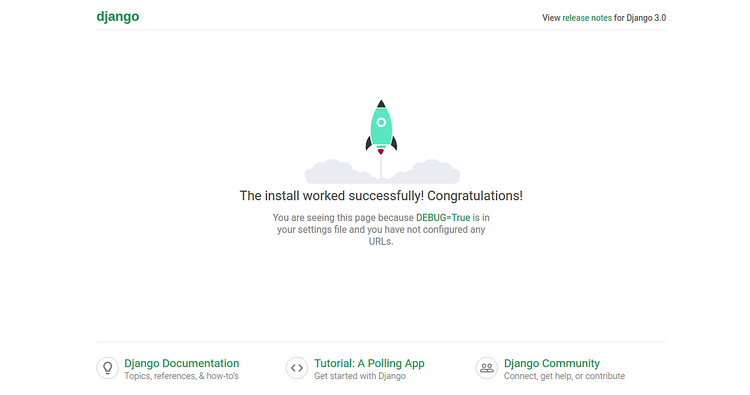
您还可以使用URL http:// your-server-ip:8000 / admin访问Django管理界面。您应该看到以下页面:
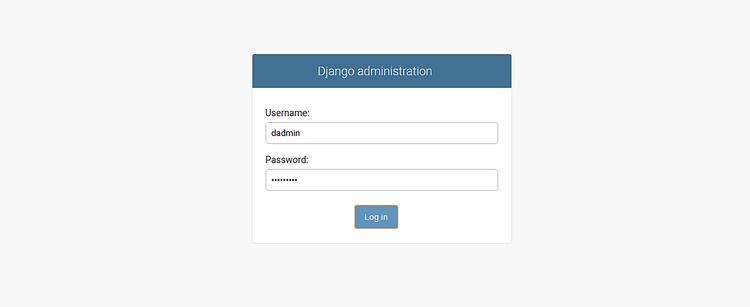
提供您的管理员用户名,密码,然后单击“ 登录 ”按钮。您应该看到以下页面:
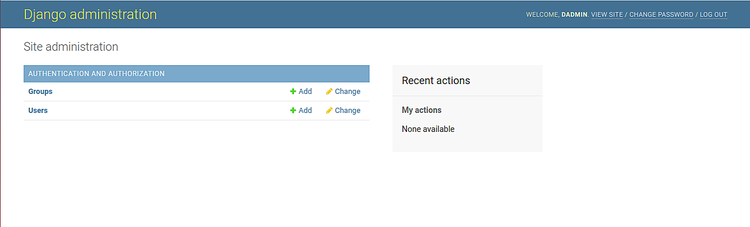
安装Nginx和Gunicorn
在本节中,我们将安装Gunicorn来创建和管理Django服务,并安装Nginx来服务Django应用程序。
首先,使用以下命令安装Nginx:
dnf install nginx -y接下来,使用PIP命令安装Gunicorn,如下所示:
pip3 install gunicorn一旦安装了两个软件包,请启动Nginx服务,并使用以下命令在系统重启后使其启动:
systemctl start nginx
systemctl enable nginx接下来,将/ opt / djangoproject目录的所有权更改为Nginx,如下所示:
chown -R nginx:nginx /opt/djangoproject为Django创建系统服务文件
接下来,使用以下命令创建用于管理Django服务的systemd服务文件:
nano /etc/systemd/system/django.service添加以下行:
[Unit] Description=django daemon After=network.target [Service] User=nginx Group=nginx WorkingDirectory=/opt/djangoproject ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/gunicorn --workers 3 --bind unix:/opt/djangoproject/djangoproject.sock djangoproject.wsgi:application [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
保存并关闭文件,然后使用以下命令重新加载systemd守护程序:
systemctl daemon-reload接下来,启动Django服务,并使用以下命令使其在系统重启后启动:
systemctl start django
systemctl enable django您现在可以使用以下命令检查Django服务的状态:
systemctl status django您应该看到以下输出:
? django.service - django daemon
Loaded: loaded (/etc/systemd/system/django.service; disabled; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: active (running) since Mon 2020-03-02 22:27:51 EST; 3min 32s ago
Main PID: 960 (django)
Tasks: 4 (limit: 25028)
Memory: 95.2M
CGroup: /system.slice/django.service
??960 /usr/bin/python3.6 /usr/local/bin/gunicorn --workers 3 --bind unix:/opt/djangoproject/djangoproject.sock djangoproject.wsgi:a>
??964 /usr/bin/python3.6 /usr/local/bin/gunicorn --workers 3 --bind unix:/opt/djangoproject/djangoproject.sock djangoproject.wsgi:a>
??965 /usr/bin/python3.6 /usr/local/bin/gunicorn --workers 3 --bind unix:/opt/djangoproject/djangoproject.sock djangoproject.wsgi:a>
??966 /usr/bin/python3.6 /usr/local/bin/gunicorn --workers 3 --bind unix:/opt/djangoproject/djangoproject.sock djangoproject.wsgi:a>
Mar 02 22:27:51 centos8 systemd[1]: Started django daemon.
Mar 02 22:27:52 centos8 django[960]: [2020-03-02 22:27:52 -0500] [960] [INFO] Starting django 20.0.4
Mar 02 22:27:52 centos8 django[960]: [2020-03-02 22:27:52 -0500] [960] [INFO] Listening at: unix:/opt/djangoproject/djangoproject.sock (960)
Mar 02 22:27:52 centos8 django[960]: [2020-03-02 22:27:52 -0500] [960] [INFO] Using worker: sync
Mar 02 22:27:52 centos8 django[960]: [2020-03-02 22:27:52 -0500] [964] [INFO] Booting worker with pid: 964
Mar 02 22:27:52 centos8 django[960]: [2020-03-02 22:27:52 -0500] [965] [INFO] Booting worker with pid: 965
Mar 02 22:27:52 centos8 django[960]: [2020-03-02 22:27:52 -0500] [966] [INFO] Booting worker with pid: 966
h pid: 966
为Django配置Nginx
接下来,您需要将Nginx配置为Django的反向代理。为此,请使用以下命令创建一个新的Nginx配置文件:
nano /etc/nginx/conf.d/django.conf添加以下行:
server {
listen 80;
server_name your-server-ip
location = /favicon.ico { access_log off; log_not_found off; }
location /static/ {
root /opt/djangoproject;
}
location / {
proxy_set_header Host $http_host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
proxy_pass http://unix:/opt/djangoproject/djangoproject.sock;
}
}
完成后保存并关闭文件。然后,使用以下命令测试nginx是否存在语法错误:
nginx -t如果一切正常,您应该获得以下输出:
nginx: the configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf syntax is ok nginx: configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf test is successful
接下来,重新启动Nginx服务以实现更改:
systemctl start nginx您还可以使用以下命令验证Nginx:
systemctl status nginx您应该获得以下输出:
? nginx.service - The nginx HTTP and reverse proxy server
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/nginx.service; disabled; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: active (running) since Mon 2020-03-02 22:28:13 EST; 4min 14s ago
Process: 984 ExecStart=/usr/sbin/nginx (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Process: 982 ExecStartPre=/usr/sbin/nginx -t (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Process: 980 ExecStartPre=/usr/bin/rm -f /run/nginx.pid (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Main PID: 985 (nginx)
Tasks: 3 (limit: 25028)
Memory: 5.5M
CGroup: /system.slice/nginx.service
??985 nginx: master process /usr/sbin/nginx
??986 nginx: worker process
??987 nginx: worker process
Mar 02 22:28:12 centos8 systemd[1]: Starting The nginx HTTP and reverse proxy server...
Mar 02 22:28:12 centos8 nginx[982]: nginx: the configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf syntax is ok
Mar 02 22:28:12 centos8 nginx[982]: nginx: configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf test is successful
Mar 02 22:28:13 centos8 systemd[1]: Started The nginx HTTP and reverse proxy server.
现在,您可以使用URL http:// your-server-ip访问Django应用程序。
结论
在本指南中,我们学习了如何在CentOS 8上安装Django。我们还学习了如何使用Gunicorn创建和管理Django服务,以及如何将Nginx配置为服务Django应用程序的反向代理。
